Over-Pronation Treatments And Causes
Excessive pronation hampers our natural walking pattern, causing an imbalance and leading to wear and tear in other parts of the body, with every step we take! Whether you have a true flat foot or suffer from over-pronation in both cases your poor walking pattern may contribute to a range of different complaints. Especially with age, poor alignment of the feet will cause very common conditions such as heel pain or knee Pain.

Causes
Over-pronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding additional stress to other parts of the foot. Therefore over-pronation can often lead to a case of Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions. There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. People with flat feet often do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.
Symptoms
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. The associated conditions depend on the individual lifestyle of each patient. Here is a list of some of the conditions associated with Over Pronation. Hallux Abducto Valgus (bunions). Hallux Rigidus (stiff 1st toe). Arch Pain. Heel Pain (plantar fascitis). Metatarsalgia (ball of the foot pain). Ankle sprains. Shin Splints. Achilles Tendonitis. Osteochondrosis. Knee Pain. Corns & Calluses. Flat Feet. Hammer Toes.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.

Non Surgical Treatment
Orthotics are medical devices used to provide support to correct a physical abnormality. They can provide arch support when needed to remedy over-pronation, and in this particular cases the orthoses used are usually convenient shoe inserts. These can be taken in and out of shoes, and will be carefully tailored by your podiatrist to the specifics of your foot. It can take some weeks before the effects of the inserts can become truly noticeable, and in many cases your podiatrist will want to review your orthotics within a few weeks to make fine adjustments based on how well they have worked to reduce your pain.
Prevention
Massage and stretch the calves to increase dorsiflexion at the foot/ankle. Dorsiflexion is the bending at the ankle. By improving the dorsiflexion, one will have more flexibility at the ankle, which will allow the foot to over-pronate less. Massage the IT Band with a foam roller or tennis ball to quiet down the tightness throughout this part of the leg. The IT Band attaches from the glute maximus and runs down the side of the leg into the knee area. When the IT Band is tight it will accelerate the force of the leg moving inward, which will cause the foot to move inward as well. It is often that tightness through the IT Band that promotes over-pronation. Decreasing over-pronation, which is very prominent in runners, will help add endurance, speed and efficiency to your run and ultimately place less stress on your body.
Coping With Severs Disease
Although the name might sound pretty frightening, Sever's disease is really a common heel injury that occurs in kids. It can be painful, but is only temporary and has no long-term effects. Calcaneal apophysitis is a painful inflammation of the heel?s growth plate. It typically affects children between the ages of 8 and 14 years old, because the heel bone (calcaneus) is not fully developed until at least age 14. Until then, new bone is forming at the growth plate (physis), a weak area located at the back of the heel. When there is too much repetitive stress on the growth plate, inflammation can develop. Calcaneal apophysitis is also called Sever?s disease, although it is not a true ?disease.? It is the most common cause of heel pain in children, and can occur in one or both feet. Heel pain in children differs from the most common type of heel pain experienced by adults. While heel pain in adults usually subsides after a period of walking, pediatric heel pain generally doesn?t improve in this manner. In fact, walking typically makes the pain worse.
Causes
The heel bone grows faster than the ligaments in the leg. As a result, muscles and tendons can become very tight and overstretched in children who are going through growth spurts. The heel is especially susceptible to injury since the foot is one of the first parts of the body to grow to full size and the heel area is not very flexible. Sever?s disease occurs as a result of repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon. Over time, this constant pressure on the already tight heel cord can damage the growth plate, causing pain and inflammation. Such stress and pressure can result from, Sports that involve running and jumping on hard surfaces (track, basketball and gymnastics). Standing too long, which puts constant pressure on the heel. Poor-fitting shoes that don?t provide enough support or padding for the feet. Overuse or exercising too much can also cause Sever?s disease.
Symptoms
Sever condition causes pain at the back of the heel. The pain is increased with plantar flexion of the ankle (pushing down with the foot as if stepping on the gas), particularly against resistance. Sever condition also causes tenderness and swelling in the area of the pain.
Diagnosis
All medical diagnosis should be made by taking a full history, examining the patient then performing investigations. The problem usually occurs in boys who are going through or have just gone through a growth spurt; one or both heels may be affected. Initially the pain may be intermittent occurring only during or after exercise. As the problem gets worse, pain may be present most of the time. There may be swelling over the back of the heel and this area is painful if touched or knocked. On examination the patient often has flat feet, very tight legs muscles especially the gastrocnemius.
Non Surgical Treatment
See a Podiatrist. Minimise inflammation, by the use of ice, rest and reduction of activity. Minimise pain with the use of anti-inflammatory medications. Shoes have been shown to attenuate shock and reduce impact on the heel. Effective cushioning in the rear through specifcally placed cushioning units, such as GEL under the heel. A 10mm heel gradient that creates a more efficient foot posture and therefore reducing strain on the lower limb. Sever's is self limiting and only possible when the growth plate is still present, and does not exist once the growth plates have closed. Podiatrists have an important role to play in preventing and managing foot problems. Prompt action is important. Problems which are left without assessment or treatment may result in major health risks.
Recovery
It may take several weeks or months for the pain to completely stop. When the pain is completely gone, your child may slowly return to his or her previous level of activity.
Does Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Call For Surgical Pocedures ?
Overview
Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency (also called posterior tibial tendon dysfunction or adult acquired flatfoot) has been named literally after failure of the posterior tibial tendon. However, the condition is caused not only by the progressive failure of the posterior tibial tendon; it is also failure of associated ligaments and joints on the inner side of the ankle and foot. This results in collapse of the arch of the foot, along with the deformity which most often becomes the debilitating problem in its later stages. While at the beginning the common symptom is pain over the tendon in the inner part of the hindfoot and midfoot, later on it is the deformity that can threaten a person?s ability to walk. Just as the tendon degenerates and loses its function, other soft tissue on the same inner side of the foot - namely the ligaments - degenerate and fail. Ligaments are responsible for holding bones in place, and when they fail, bones shift to places where they shouldn?t; deformity is the result. The deformity causes malalignment, leading to more stress and failure of the ligaments. 
Causes
Overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. In fact, the symptoms usually occur after activities that involve the tendon, such as running, walking, hiking, or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
Initially, flatfoot deformity may not present with any symptoms. However, overtime as the tendon continues to function in an abnormal position, people with fallen arches will begin to have throbbing or sharp pain along the inside of the arch. Once the tendon and soft tissue around it elongates, there is no strengthening exercises or mechanism to shorten the tendon back to a normal position. Flatfoot can also occur in one or both feet. If the arch starts to slowly collapse in one foot and not the other, posterior tibial dysfunction (PTTD) is the most likely cause. People with flatfoot may only have pain with certain activities such as running or exercise in the early phase of PTTD. Pain may start from the arch and continue towards the inside part of the foot and ankle where the tendon courses from the leg. Redness, swelling and increased warmth may also occur. Later signs of PTTD include pain on the outside of the foot from the arch collapsing and impinging other joints. Arthritic symptoms such as painful, swollen joints in the foot and ankle may occur later as well due to the increased stress on the joints from working in an abnormal position for a long period of time.
Diagnosis
Although you can do the "wet test" at home, a thorough examination by a doctor will be needed to identify why the flatfoot developed. Possible causes include a congenital abnormality, a bone fracture or dislocation, a torn or stretched tendon, arthritis or neurologic weakness. For example, an inability to rise up on your toes while standing on the affected foot may indicate damage to the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which supports the heel and forms the arch. If "too many toes" show on the outside of your foot when the doctor views you from the rear, your shinbone (tibia) may be sliding off the anklebone (talus), another indicator of damage to the PTT. Be sure to wear your regular shoes to the examination. An irregular wear pattern on the bottom of the shoe is another indicator of acquired adult flatfoot. Your physician may request X-rays to see how the bones of your feet are aligned. Muscle and tendon strength are tested by asking you to move the foot while the doctor holds it.
Non surgical Treatment
It is imperative that you seek treatment should you notice any symptoms of a falling arch or PTTD. Due to the progressive nature of this condition, your foot will have a much higher chance of staying strong and healthy with early treatment. When pain first appears, your doctor will evaluate your foot to confirm a flatfoot diagnosis and begin an appropriate treatment plan. This may involve rest, anti-inflammatory medications, shoe modifications, physical therapy, orthotics and a possible boot or brace. When treatment can be applied at the beginning, symptoms can most often be resolved without the need for surgery. 
Surgical Treatment
If initial conservative therapy of posterior tibial tendon insufficiency fails, surgical treatment is considered. Operative treatment of stage 1 disease involves release of the tendon sheath, tenosynovectomy, debridement of the tendon with excision of flap tears, and repair of longitudinal tears. A short-leg walking cast is worn for 3 weeks postoperatively. Teasdall and Johnson reported complete relief of pain in 74% of 14 patients undergoing this treatment regimen for stage 1 disease. Surgical debridement of tenosynovitis in early stages is believed to possibly prevent progression of disease to later stages of dysfunction.
What Are The Causes Of Heel Aches

Plantar Heel Pain is a commonly encountered orthopedic problem that can cause significant discomfort and a limp because of the difficulty in bearing weight. The etiologies of this condition are multiple; therefore, a careful clinical evaluation is necessary for its appropriate management. Nonsurgical or conservative care is successful in most cases.
Causes
Heel pain sometimes results from excessive pronation. Pronation is the normal flexible motion and flattening of the arch of the foot that allows it to adapt to ground surfaces and absorb shock in the normal walking pattern. As you walk, the heel contacts the ground first; the weight shifts first to the outside of the foot, then moves toward the big toe. The arch rises, the foot generally rolls upward and outward, becoming rigid and stable in order to lift the body and move it forward. Excessive pronation-excessive inward motion-can create an abnormal amount of stretching and pulling on the ligaments and tendons attaching to the bottom back of the heel bone. Excessive pronation may also contribute to injury to the hip, knee, and lower back.
Symptoms
Common symptoms, heel Spurs: the pain is usually worst on standing, particularly first thing in the morning when you get up. It is relatively common, though usually occurring in the over forty's age group. There are no visible features on the heel but a deep localised painful spot can be found in or around the middle of the sole of the heel. Although it is often associated with a spur of bone sticking out of the heel bone (heel spur syndrome), approximately ten per cent of the population have heel spurs without any pain. Heel Bursitis, pain can be felt at the back of the heel when the ankle joint is moved and there may be a swelling on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Or you may feel pain deep inside the heel when it makes contact with the ground. Heel Bumps, recognised as firm bumps on the back of the heel , they are often rubbed by shoes causing pain.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for plantar fasciitis should be directed at resting the plantar fascia, providing support for the arch area and limiting pronation. This is often accomplished with the use of supportive strapping with athletic tape, arch supports and orthotics. Heel lifts may also be helpful. Anti-inflammatories, pills as well as cortisone injections, may be effective as an adjunctive treatment by speeding up the reduction of inflammation. However, if used alone, anti-inflammatories rarely lead to resolution of the condition. Stretching exercises, physical therapy and night splints may also be helpful. The majority of cases respond to non-surgical treatment although it may take several weeks to reach a comfortable level. In those cases that do not respond adequately to conservative measures, surgical release of the plantar fascia may be considered. However, a new non-surgical treatment called Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is now available as an option for recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. ESWT was approved by the FDA recently for the treatment of chronic heel pain. It has been in use for several years on thousands of patients in Europe and has been successfully used to restore patients with chronic plantar fasciitis to a normal, active lifestyle. ESWT is a non-invasive procedure that uses high intensity sound waves similar to what is routinely used to treat kidney stones. The treatment is usually performed in the office or in an outpatient surgical center. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes about 25 minutes. The shockwaves are directed at the plantar fascia and stimulate an inflammatory healing response.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
Prevention

The following steps will help prevent plantar fasciitis or help keep the condition from getting worse if you already have it. The primary treatment is rest. Cold packs application to the area for 20 minutes several times a day or after activities give some relief. Over-the-counter pain medications can help manage the pain, consult your healthcare professional. Shoes should be well cushioned, especially in the midsole area, and should have the appropriate arch support. Some will benefit from an orthotic shoe insert, such as a rubber heel pad for cushioning. Orthotics should be used in both shoes, even if only one foot hurts. Going barefoot or wearing slipper puts stress on your feet. Put on supportive shoes as soon as you get out of bed. Calf stretches and stretches using a towel (place the towel under the ball of your feet and pull gently the towel toward you and hold a few seconds) several times a day, especially when first getting up in the morning. Stretching the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel is especially important before sports, but it is helpful for nonathletes as well. Increasing your exercise levels gradually. Staying at a healthy weight. Surgery is very rarely required.
What Is The Big Cause Of Achilles Tendon Pain ?
 This nagging injury can be long-lasting if not treated - and if your running form needs some work. The name Achilles is said to be a combination of two Greek words that together mean ?grief of the people.? The injury that bears that hero?s name, in honor of his only weakness, certainly aggrieves many runners, with Achilles tendinitis accounting for around 10 percent of running injuries. Technically, Achilles tendinitis is acute inflammation of the tendon that runs along the back of the ankle. Pain in that area for longer than a couple weeks is not really tendinitis anymore. Athletes, however, tend to characterize any pain along the tendon above the back of the heel as Achilles tendinitis. Achilles tendinitis can be confused with other injuries, such as heel problems, but the hallmark sign is if you?re pinching the Achilles and it?s really sore.
This nagging injury can be long-lasting if not treated - and if your running form needs some work. The name Achilles is said to be a combination of two Greek words that together mean ?grief of the people.? The injury that bears that hero?s name, in honor of his only weakness, certainly aggrieves many runners, with Achilles tendinitis accounting for around 10 percent of running injuries. Technically, Achilles tendinitis is acute inflammation of the tendon that runs along the back of the ankle. Pain in that area for longer than a couple weeks is not really tendinitis anymore. Athletes, however, tend to characterize any pain along the tendon above the back of the heel as Achilles tendinitis. Achilles tendinitis can be confused with other injuries, such as heel problems, but the hallmark sign is if you?re pinching the Achilles and it?s really sore.
Causes
Hill running or stair climbing. Overuse resulting from the natural lack of flexibility in the calf muscles. Rapidly increasing mileage or speed. Starting up too quickly after a layoff. Trauma caused by sudden and hard contraction of the calf muscles when putting out extra effort such as in a final sprint. Achilles tendinitis often begins with mild pain after exercise or running that gradually worsens.
Symptoms
People with Achilles tendinitis may experience pain during and after exercising. Running and jumping activities become painful and difficult. Symptoms include stiffness and pain in the back of the ankle when pushing off the ball of the foot. For patients with chronic tendinitis (longer than six weeks), x-rays may reveal calcification (hardening of the tissue) in the tendon. Chronic tendinitis can result in a breakdown of the tendon, or tendinosis, which weakens the tendon and may cause a rupture.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist can usually make the diagnosis by clinical history and physical examination alone. Pain with touching or stretching the tendon is typical. There may also be a visible swelling to the tendon. The patient frequently has difficulty plantarflexing (pushing down the ball of the foot and toes, like one would press on a gas pedal), particularly against resistance. In most cases X-rays don't show much, as they tend to show bone more than soft tissues. But X-rays may show associated degeneration of the heel bone that is common with Achilles Tendon problems. For example, heel spurs, calcification within the tendon, avulsion fractures, periostitis (a bruising of the outer covering of the bone) may all be seen on X-ray. In cases where we are uncertain as to the extent of the damage to the tendon, though, an MRI scan may be necessary, which images the soft tissues better than X-rays. When the tendon is simply inflamed and not severely damaged, the problem may or may not be visible on MRI. It depends upon the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment will focus on relieving the pain and preventing further injury. Your podiatrist may create shoe inserts or a soft cast to effectively immobilize the affected area for a period of time. (Often, a couple of weeks are needed for the tendon to heal.) Medication can help too. Your podiatrist may recommend or prescribe oral medication.

Surgical Treatment
Many people don't realize that Achilles tendon surgery can be very traumatic to your body. The type of trauma you experience after surgery can be compared to what you go through when you first injured your Achilles tendon. During the first 24 to 72 hours after the surgery your ankle will be tender, swollen and very painful. Your leg will be weak and unstable making it impossible for you to put weight on your leg without some kind of help. This is why your doctor or surgeon will have you outfitted for a cast, ankle brace and/or crutches before the procedure. When you are relying on a cast/brace and crutches your Achilles tendon is less likely to be as active as it once was. This is usually why atrophy (loss) of your lower leg muscles (specifically your calf muscle) happens. In general, more than 80%* of people who undergo surgery for an injured Achilles Tendon are able to return to their active lifestyle. In order to avoid re-injury, it is important to commit to a regular conservative therapy routine.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent Achilles tendinitis, you can take measures to reduce your risk. Increase your activity level gradually. If you're just beginning an exercise regimen, start slowly and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the training. Take it easy. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your tendons, such as hill running. If you participate in a strenuous activity, warm up first by exercising at a slower pace. If you notice pain during a particular exercise, stop and rest. Choose your shoes carefully. The shoes you wear while exercising should provide adequate cushioning for your heel and should have a firm arch support to help reduce the tension in the Achilles tendon. Replace your worn-out shoes. If your shoes are in good condition but don't support your feet, try arch supports in both shoes. Stretch daily. Take the time to stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon in the morning, before exercise and after exercise to maintain flexibility. This is especially important to avoid a recurrence of Achilles tendinitis. Strengthen your calf muscles. Strong calf muscles enable the calf and Achilles tendon to better handle the stresses they encounter with activity and exercise. Cross-train. Alternate high-impact activities, such as running and jumping, with low-impact activities, such as cycling and swimming.
What Is Painful Heel And Best Ways To Fix It

Overview
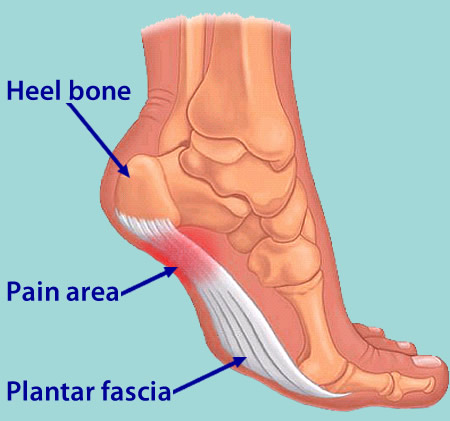
The plantar fascia is a thickened fibrous aponeurosis that originates from the medial tubercle of the calcaneus, runs forward to insert into the deep, short transverse ligaments of the metatarsal heads, dividing into 5 digital bands at the metatarsophalangeal joints and continuing forward to form the fibrous flexor sheathes on the plantar aspect of the toes. Small plantar nerves are invested in and around the plantar fascia, acting to register and mediate pain.
Causes
You're more likely to develop the condition if you're female, overweight or have a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces. You're also at risk if you walk or run for exercise, especially if you have tight calf muscles that limit how far you can flex your ankles. People with very flat feet or very high arches also are more prone to plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Most people with plantar fasciitis have pain when they take their first steps after they get out of bed or sit for a long time. You may have less stiffness and pain after you take a few steps. But your foot may hurt more as the day goes on. It may hurt the most when you climb stairs or after you stand for a long time. If you have foot pain at night, you may have a different problem, such as arthritis , or a nerve problem such as tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can usually diagnose plantar fasciitis just by talking to you and examining your feet. Rarely, tests are needed if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other possible causes of heel pain. These can include X-rays of the heel or an ultrasound scan of the fascia. An ultrasound scan usually shows thickening and swelling of the fascia in plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter Orthotics. A soft, over-the-counter orthotic (Prefabricated orthotic) with an accommodating arch support has proven to be quite helpful in the management of plantar fascia symptoms. Studies demonstrate that it is NOT necessary to obtain a custom orthotic for the treatment of this problem. Comfort Shoes. Shoes with a stiff sole, rocker-bottom contour, and a comfortable leather upper combined with an over-the-counter orthotic or a padded heel can be very helpful in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Anti-Inflammatory Medication (NSAIDs): A short course of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be helpful in managing plantar fasciitis symptoms providing the patient does not have any contra-indications such as a history of stomach ulcers. Activity Modification Any activity that has recently been started, such as a new running routine or a new exercise at the gym that may have increased loading through the heel area, should be stopped on a temporary basis until the symptoms have resolved. At that point, these activities can be gradually started again. Also, any activity changes (ex. sitting more) that will limit the amount of time a patient is on their feet each day may be helpful. A night splint, which keeps the ankle in a neutral position (right angle) while the patient sleeps, can be very helpful in alleviating the significant morning symptoms. A night splint may be prescribed by your physician. Alternatively, it can be ordered online or even obtained in some medical supply stores. This splint is worn nightly for 1-3 weeks until the cycle of pain is broken. Furthermore, this splinting can be reinstituted for a short period of time is symptoms recur.

Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
What Causes Pain Of The Heel And The Way To Heal It

Overview
If you experience sharp, throbbing or aching heel pain with your first steps out of bed each morning, or when walking throughout the day, you may be suffering from Plantar Fasciitis. This guide will help you to understand the definition, symptoms and causes of this condition and will explore your treatment options for rapid relief from your pain.
Causes
A number of factors can contribute to plantar fasciitis. While men can get plantar fasciitis, it is more common in women. You're also more likely to have this condition as you age or if you are overweight. Take up a new form of exercise or suddenly increase the intensity of your exercise. Are on your feet for several hours each day. Have other medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus). Tend to wear high-heeled shoes, and then switch abruptly to flat shoes. Wear shoes that are worn out with weak arch supports and thin soles. Have flat feet or an unusually high arch. Have legs of uneven lengths or an abnormal walk or foot position. Have tight achilles tendons, or ‘heel cords’.
Symptoms
The classic sign of plantar fasciitis is that the worst pain occurs with the first few steps in the morning, but not every patient will have this symptom. Patients often notice pain at the beginning of activity that lessens or resolves as they warm up. The pain may also occur with prolonged standing and is sometimes accompanied by stiffness. In more severe cases, the pain will also worsen toward the end of the day.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can usually diagnose plantar fasciitis just by talking to you and examining your feet. Rarely, tests are needed if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other possible causes of heel pain. These can include X-rays of the heel or an ultrasound scan of the fascia. An ultrasound scan usually shows thickening and swelling of the fascia in plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are several things you can do to self-treat your heel or arch pain. The first thing is to wear better shoes and consider adding arch supports or custom foot orthotics to your shoes. Stretching the calf muscles can also often be helpful. Try to stretch when you first get up in the morning and before you go to bed at night. Another good exercise is to "roll" your arch and heel. This is done by placing a tennis ball, golf ball, or lacrosse ball on the floor and rolling your foot on top of it. Some people get extra benefit by "rolling" on a frozen water bottle. You should also carefully evaluate your fitness program as you may be overdoing it. You may want consider backing of new or recently added exercises or increases in training until your heel pain improves. If you work at a standing job try to take more time to walk around during the day and avoid standing in one place for too long.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.